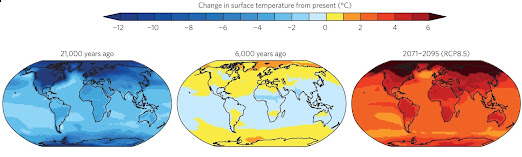
Climate change refers to long-term changes in temperature, weather patterns, and other aspects of Earth’s climate. These changes are primarily driven by human activities, such as the burning of fossil fuels and deforestation, which release greenhouse gases into the atmosphere. Here are some examples of the effects and manifestations of climate change examples :
Climate Change Examples In Global Warming
Rising Temperatures: Global temperatures are increasing, leading to more frequent and severe heatwaves. For example, record-breaking high temperatures have been observed in many parts of the world Global warming.
Melting Glaciers and Ice Sheets: As temperatures rise, glaciers and polar ice sheets are melting at an accelerating rate. This contributes to rising sea levels, which can lead to coastal flooding.
Sea-Level Rise: Rising temperatures cause seawater to expand, and the melting of ice adds more water to the oceans. This leads to rising sea levels, threatening coastal communities and ecosystems.
Ocean Acidification: The absorption of excess carbon dioxide by the world’s oceans is causing them to become more acidic. This has a negative impact on marine life, particularly organisms with calcium carbonate shells, like corals and some types of plankton.
Extreme Weather Events: Climate change is linked to an increase in the frequency and severity of extreme weather events, such as hurricanes, droughts, floods, and wildfires. For example, stronger hurricanes and more intense wildfires have been observed in various regions.
Altered Rainfall Patterns: Climate change can disrupt traditional rainfall patterns. Some areas may experience more frequent and severe droughts, while others may face increased rainfall and flooding.
Shifts in Ecosystems: Rising temperatures are causing shifts in ecosystems. Species may move to higher altitudes or latitudes to find suitable habitats. This can disrupt existing ecosystems and lead to imbalances in local biodiversity.
Threats to Food Security: Climate change can affect crop yields and food production. Extreme weather events and changing temperature and precipitation patterns can impact agricultural productivity and food security.
Health Impacts: Climate change can have direct and indirect health impacts. Heat-related illnesses, the spread of disease-carrying vectors like mosquitoes, and reduced air quality due to increased wildfires are examples of health-related consequences.
Loss of Biodiversity: Climate change poses a significant threat to biodiversity. Habitats are changing, and some species may struggle to adapt or may face increased risks of extinction.
Displacement of Communities: Rising sea levels, extreme weather events, and environmental changes can force communities to relocate, leading to climate-induced migration and displacement.
These examples illustrate the diverse and far-reaching impacts of climate change. It is a global challenge that requires concerted efforts to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, adapt to its effects, and mitigate its most severe consequences.








