Global warming is having a significant impact on summers around the world, and it is manifesting itself differently in different regions. Some of the main impacts include:
Global Warming Summer Effects In The World | Sudden Climate Change In World Wide
1. Heatwaves
Increased Frequency and Intensity: More frequent and severe heatwaves can lead to health problems such as heat stroke and dehydration, especially in vulnerable populations.
Urban Heat Islands: Cities can become hotter than rural areas due to human activities and heat trapped by buildings.
2. Wildfire
Increased Risk: Extended periods of heat and drought increase the risk of wildfires, which can destroy ecosystems, property and air quality.
Longer Fire Seasons: Fire seasons are getting longer, putting additional strain on firefighting resources and resulting in more frequent and larger fires.
3. Drought
Impacts on Agriculture: Extended droughts can lead to crop failures, affecting food supplies and prices.
Water Shortages: Reduced water availability affects drinking water supplies and irrigation, leading to conflicts over water resources.
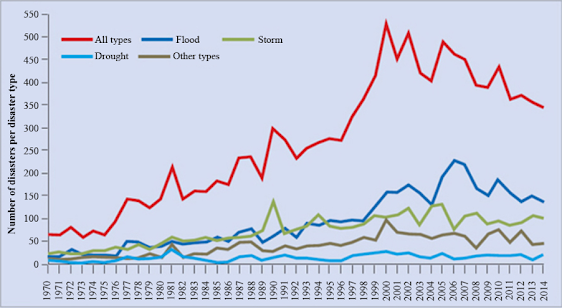
4. Storms and Floods
Increased Storm Intensity: Rising temperatures can result in more intense storms, such as hurricanes and typhoons, which can cause significant damage.
Flooding: Melting glaciers and ice sheets and increased precipitation contribute to sea level rise and flooding, especially in coastal and low-lying areas.
5. Ecosystem Destruction
Habitat Change: Changes in temperature and precipitation patterns can destroy habitats, causing shifts in species distribution and possible extinction.
Coral Bleaching: Rising ocean temperatures can cause coral bleaching, threatening marine biodiversity.
6. Health Issues
Heat-Related Diseases: Higher temperatures can worsen respiratory and cardiovascular diseases.
Vector-Borne Diseases: Warmer weather can increase the spread of diseases such as malaria and dengue fever because mosquitoes and other vectors thrive in high temperatures.
7. Economic Impacts
Agriculture: Crop yields fall and irrigation costs increase.
Energy Requirements: Higher energy consumption for cooling increases costs and puts strain on the power grid.
Tourism: Extreme weather conditions may make travel destinations less attractive.
Regional Examples
North America: More frequent and intense wildfires in the Western US and Canada, severe heat waves and droughts affect agriculture in the Midwest.
Europe: Heat waves cause many deaths, droughts affect Southern Europe, and the risk of forest fires increases in the Mediterranean region.
Asia: Increased monsoon rains are causing floods and heatwaves in South Asia and typhoons in East and Southeast Asia.
Africa: Severe droughts in the Sahel and Horn of Africa are affecting food security and water resources.
Australia: Record temperatures are causing forest fires and coral bleaching on the Great Barrier Reef.
Strong climate adaptation and mitigation strategies are needed to address the impacts of global warming in summer, including reducing greenhouse gas emissions, improving water management, and improving emergency preparedness and response systems.