Climate change has significant and wide-ranging impacts on agriculture, affecting everything from crop yields to livestock production and food security. These impacts are often negative and pose considerable challenges to global food production. Here are some of the key ways in which impact of climate change on agriculture
impact of climate change on agriculture Global warming
Altered Growing Seasons: Climate change can disrupt traditional growing seasons by changing temperature and precipitation patterns. Warmer winters can lead to earlier spring planting, but this can also expose crops to late spring frosts. Erratic rainfall patterns can make it difficult for farmers to predict when to plant and harvest, affecting crop yields and quality.
Reduced Crop Yields: Increased temperatures, heatwaves, and prolonged periods of drought can stress crops and reduce their yields. High temperatures during critical growth stages can cause heat stress in many crops, leading to decreased yields.
Increased Pest and Disease Pressure: Rising temperatures can expand the range of pests and diseases that affect crops and livestock. This can lead to increased outbreaks and the need for more pesticides and treatments, increasing production costs.
Water Scarcity: Climate change can exacerbate water scarcity issues, affecting irrigation practices and the availability of water for agriculture. In regions dependent on seasonal rainfall or glacial meltwater, water shortages can have a severe impact on crop production.
Loss of Livestock Productivity: Heat stress can reduce livestock productivity, including milk and meat production. Livestock are also vulnerable to diseases that thrive in warmer conditions.
Shifts in Suitable Crop Areas: Changing temperature and precipitation patterns can lead to shifts in the suitability of certain crops in specific regions. Farmers may need to adapt by changing the types of crops they grow.
Increased Extreme Weather Events: Climate change is associated with more frequent and severe extreme weather events, such as hurricanes, floods, and droughts. These events can damage crops, infrastructure, and disrupt supply chains.
Soil Degradation: Changes in temperature and precipitation patterns can lead to soil degradation, erosion, and reduced soil fertility, making it more challenging for farmers to maintain productive agricultural land.
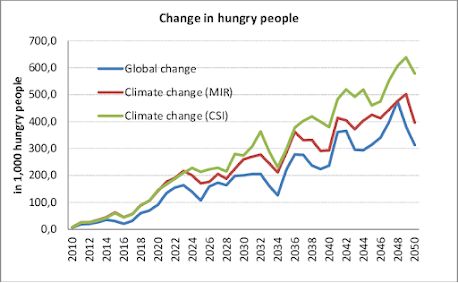
Food Security: The cumulative effect of these challenges can threaten food security, particularly in vulnerable regions where agriculture is a primary source of food and livelihoods.
Economic Impacts: Climate-related disruptions in agriculture can have economic consequences, affecting farmers’ incomes, rural communities, and global food prices.
To address the impact of climate change on agriculture, adaptation and mitigation strategies are essential
Climate-Resilient Crop Varieties: Developing and adopting crop varieties that are more resilient to changing climate conditions and extreme weather events.
Improved Irrigation Practices: Implementing efficient and sustainable irrigation techniques to mitigate water scarcity.
Sustainable Farming Practices: Promoting sustainable farming practices such as no-till farming, crop rotation, and cover cropping to conserve soil and water resources.
Weather Forecasting and Early Warning Systems: Providing farmers with accurate weather forecasts and early warning systems to help them make informed decisions about planting and harvesting.
Policy and Investment: Governments and international organizations can enact policies and provide financial support to help farmers adapt to climate change and reduce emissions from agriculture.
Research and Innovation: Investing in agricultural research and innovation to develop new technologies and practices that can improve climate resilience and reduce the carbon footprint of agriculture.
Addressing the impact of climate change on agriculture is crucial to ensuring global food security and the livelihoods of millions of people who depend on farming for their income and sustenance.





