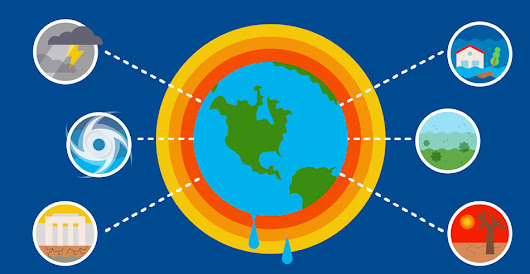
Global warming has significant impacts on the world’s water systems, including oceans, rivers, lakes, and groundwater. These impacts can have far-reaching consequences for both natural ecosystems and human societies. Some of the key effects of global warming on water are:
The Impact Of Global Warming On Water And Effects
Rising Sea Levels: The melting of polar ice caps and glaciers, along with the thermal expansion of seawater as it warms, contributes to rising sea levels. Higher sea levels can lead to coastal flooding, erosion, and the displacement of coastal communities.
Ocean Warming: Increased global temperatures lead to ocean warming. This can harm marine ecosystems, disrupt fish populations, and impact the distribution of marine species. It can also contribute to the intensification of storms.
Ocean Acidification: As the atmosphere absorbs more carbon dioxide (CO2), the oceans also absorb a significant amount, causing ocean acidification. This can negatively affect marine life, particularly organisms with calcium carbonate shells or skeletons, such as coral reefs and shellfish.
Changes in Precipitation Patterns: Global warming can alter regional precipitation patterns, leading to increased droughts in some areas and more intense rainfall in others. These changes can affect water availability for agriculture, industry, and communities.
Melting Glaciers and Snowpack: Warming temperatures cause glaciers and seasonal snowpack to melt earlier and at an accelerated rate. This can impact the availability of freshwater for drinking water, agriculture, and hydropower.
Changes in Streamflow: Altered precipitation patterns and melting snowpack can lead to changes in streamflow, potentially resulting in seasonal water shortages in some regions and increased flood risks in others.
Water Quality: Higher temperatures can affect water quality by promoting the growth of harmful algal blooms, reducing oxygen levels, and increasing the risk of waterborne diseases. Changes in water temperature can also impact the suitability of aquatic habitats for various species.
Threats to Coastal Aquifers: Rising sea levels can lead to the intrusion of saltwater into coastal aquifers, making freshwater resources brackish or unusable for agriculture or drinking.
Shifts in Ecosystems: Changes in water temperature, flow, and quality can disrupt aquatic ecosystems, affecting fish migration, spawning patterns, and the survival of many aquatic species.
Human Impacts: These water-related changes can have profound consequences for agriculture, food security, public health, and economies, especially in vulnerable regions.
Efforts to address the impact of global warming on water systems involve both mitigation (reducing greenhouse gas emissions to limit global warming) and adaptation (developing strategies to cope with the changes that are already occurring). This includes implementing water conservation measures, protecting watersheds, and developing resilient infrastructure to manage water resources effectively in a changing climate. International cooperation and policy initiatives are crucial in addressing these challenges on a global scale.





